Let’s start at the beginning; What is a DIMM (Dual Inline Memory Module)? This is the foundation of RAM over the last few decades. Even though DIMM has been the standard, it doesn’t tell the full picture. There are many types of DIMMs ,just as a refresher, let’s look over all the variants and a brief description of each.
- UDIMM (Unbuffered DIMM):
- Commonly used in consumer desktops and laptops.
- No buffer between the memory controller and the DRAM chips, offering direct access to the memory.
- RDIMM (Registered DIMM):
- Includes a register between the memory controller and the DRAM.
- Used in servers and workstations for stability and scalability.
- LRDIMM (Load-Reduced DIMM):
- Uses a memory buffer to reduce the load on the memory controller.
- Ideal for high-capacity memory configurations in servers.
- SODIMM (Small Outline DIMM):
- Smaller version of DIMMs used in laptops, notebooks, and small form-factor devices.
- Available as UDIMM, RDIMM, and other variations.
- FBDIMM (Fully Buffered DIMM):
- Utilizes an advanced memory buffer (AMB) to improve reliability and scalability.
- Mainly used in older server architectures.
- NVDIMM (Non-Volatile DIMM):
- Combines DRAM with NAND flash memory, providing non-volatile storage.
- Used for applications requiring persistent memory.
- ECC DIMM (Error-Correcting Code DIMM):
- Can detect and correct data corruption.
- Used in systems where data integrity is critical, like servers and workstations.
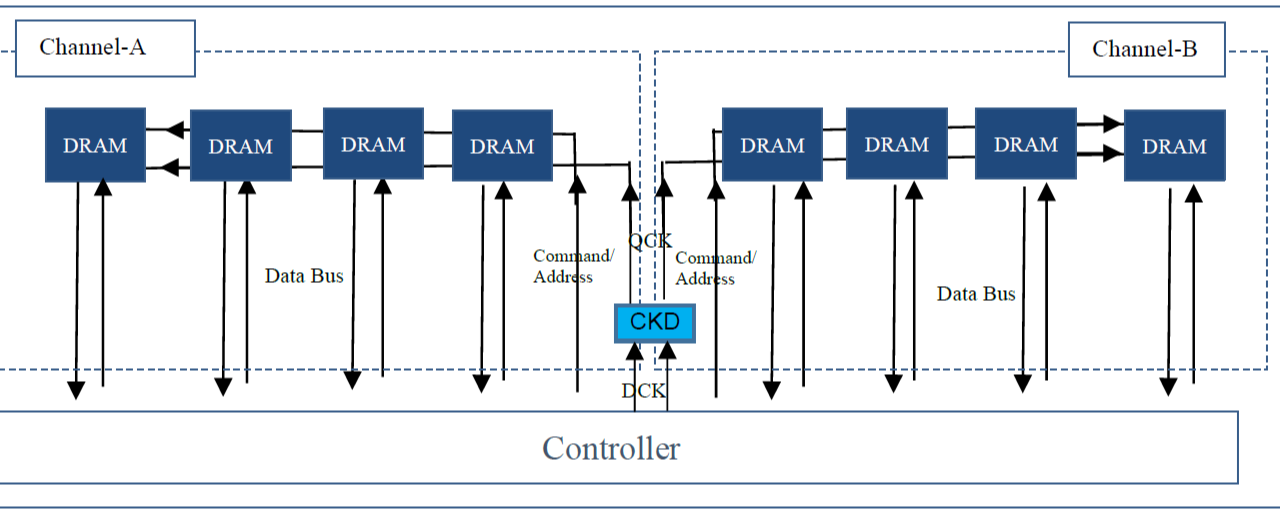
- CUDIMM (Clocked Unbuffered DIMM):
- Enhances standard UDIMM by adding a clock driver.
- Offers better signal integrity and performance.
So what does the CUDIMM really do that is going to change the desktop experience?
- Improved Signal Integrity: The inclusion of a clock driver on the CUDIMM enhances signal stability, reducing noise and jitter, which is crucial for high-speed operations.
- Higher Operating Frequencies: CUDIMMs can support higher clock speeds, allowing for faster memory performance and more stable data transfer rates.
- Reliability: The improved signal integrity and stability of CUDIMMs contribute to a more reliable memory system, which is essential for demanding applications like gaming, video editing, and scientific research.
- Overclocking Potential: The enhanced stability of CUDIMMs opens up new possibilities for overclocking, enabling users to push memory speeds even higher than before.
In essence, CUDIMM builds on the standard DIMM by adding a clock driver for enhanced performance and stability, especially at higher speeds
UDIMM (Unbuffered DIMM) and CUDIMM (Clocked Unbuffered DIMM) share the same connector on the motherboard. However, to take full advantage of CUDIMM’s enhanced performance features, you’ll need a compatible motherboard and processor that support CUDIMM technology.